Introduction to Autobà and its significance in entomology
Step into the captivating world of Autobà, a genus of moths that has intrigued entomologists and nature enthusiasts alike since its creation by Francis Walker in 1863. Join us on a journey to discover the fascinating life and characteristics of these unique creatures, as we delve into their taxonomy, distribution, behaviors, and conservation efforts. Let’s unravel the mysteries surrounding Autobà and explore why they hold a special place in the realm of entomology.
Life & Work of Francis Walker, The Creator of Autobà Genus
Francis Walker, a renowned entomologist from the 19th century, left an indelible mark on the world of taxonomy with his creation of the Autobà genus. His passion for insects and meticulous observations led him to classify and name numerous species during his lifetime.
Walker’s dedication to studying moths and butterflies allowed him to establish not only Autobà but also many other genera that are still studied today. His keen eye for detail and systematic approach laid the foundation for future generations of scientists.
Through his work, Walker contributed significantly to our understanding of biodiversity in the natural world. His legacy lives on through the continued research and exploration into the fascinating realm of Lepidoptera that he helped shape.
Taxonomy and characteristics of Autobà moths
Let’s delve into the taxonomy and unique characteristics of Autobà moths. These fascinating creatures belong to the genus Autobà, which was erected by Francis Walker in 1863. Within this genus, there are several distinct species that exhibit diverse physical attributes and behaviors.
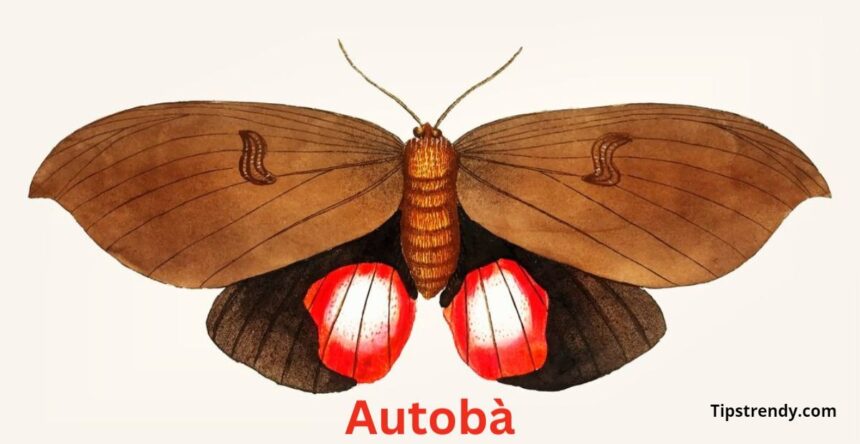
Autobà moths are known for their intricate wing patterns and vibrant colors, making them a sight to behold in the wild. Their delicate bodies are adorned with fine scales that shimmer in the sunlight, aiding in camouflage and attracting potential mates.
In terms of size, Autobà moths can vary from small to medium-sized insects, with wingspans ranging from a few centimeters to over ten centimeters. Despite their size differences, all Autobà species share common traits such as nocturnal habits and specialized feeding preferences.
These moths play a crucial role in ecosystem dynamics through pollination and serving as a food source for other organisms. As we continue to study these enigmatic insects, we uncover more about their evolutionary history and ecological significance.
Distribution and habitat of Autobà species
Autobà moths, a genus created by the renowned entomologist Francis Walker in 1863, have a diverse distribution across various regions of the world. These fascinating creatures can be found inhabiting a range of habitats, from lush tropical forests to arid deserts. The Autobà species are known for their adaptability and ability to thrive in different environments.
In North America, Autobà moths are commonly spotted in wooded areas and grasslands, while in Europe they often reside in meadows and gardens. In Asia, these unique insects can be found fluttering among mountainous regions and coastal plains. Their widespread distribution showcases the resilience of Autobà moths and their capacity to survive in diverse ecosystems.
The habitat preferences of Autobà species vary depending on factors such as climate, vegetation, and food sources. Some species prefer densely vegetated areas with abundant foliage for camouflage, while others thrive in open spaces with access to nectar-rich flowers for sustenance. Understanding the distribution patterns and habitat requirements of Autobà moths is crucial for conservation efforts aimed at protecting these remarkable insects for future generations to marvel at.
Unique behaviors and adaptations of Autobà moths
Autobà moths exhibit fascinating behaviors and remarkable adaptations that set them apart in the world of entomology. One intriguing behavior displayed by Autobà species is their nocturnal activity, taking flight under the cover of darkness to avoid predators and maximize their chances of survival. Their cryptic coloration allows them to blend seamlessly into their surroundings, evading detection by potential threats.
These moths also showcase an interesting mating ritual involving pheromone communication, where females release chemical signals to attract males for reproduction. This intricate process plays a crucial role in ensuring successful breeding within Autobà populations. Additionally, some Autobà species display unique feeding preferences, targeting specific plant species for sustenance.
In terms of adaptations, Autobà moths have developed specialized wing patterns that aid in camouflage and mimicry, providing them with a defensive advantage against predators. Their ability to adapt to diverse habitats further underscores their resilience as a genus of moths with exceptional survival strategies.
Threats to Autobà populations and conservation efforts
The Autobà genus of moths, created by Francis Walker in 1863, faces various threats to its populations today. Habitat loss due to deforestation and urban development is a significant challenge for these unique insects. Climate change also poses a threat, disrupting the delicate balance of ecosystems where Autobà species reside.
Pesticide use in agriculture can have detrimental effects on Autobà populations, impacting their food sources and breeding grounds. Additionally, light pollution from urban areas can interfere with their natural behaviors and navigation patterns. These factors combined contribute to the decline in Autobà numbers across different regions.
Conservation efforts are crucial to safeguarding the future of Autobà moths. Initiatives such as habitat restoration projects and sustainable land management practices can help mitigate the threats faced by these fascinating creatures. Collaboration between researchers, conservationists, and policymakers is essential to ensure the preservation of Autobà species for generations to come.
Future research and discoveries in the study of Autobà
As researchers delve deeper into the study of Autobà moths, there is a sense of excitement and anticipation for the future. The intricate details of their taxonomy and behavior continue to unravel new mysteries waiting to be uncovered. With advancements in technology and methodology, scientists are poised to make groundbreaking discoveries that will shed light on the evolutionary history and ecological significance of these enigmatic creatures.
Future research endeavors may focus on exploring the genetic makeup of Autobà species to understand their phylogenetic relationships better. By analyzing their DNA sequences, scientists aim to elucidate how these moths have evolved over time and adapted to various environments. Additionally, studies on the impact of climate change and habitat destruction on Autobà populations could provide valuable insights into conservation efforts for these vulnerable insects.
By combining traditional fieldwork with modern scientific techniques, researchers are paving the way for a more comprehensive understanding of Autobà moths’ biology and ecology. As we look forward to what lies ahead in the realm of entomology, one thing is certain – there is still so much more to learn about Autobà and its place in the natural world.
You Might Also Like:
- The Art of Slow Living: Rediscovering Analog Hobbies
- Suwuianna: The Ultimate Guide to Achieving Inner Peace
- A Journey to Finding Balance in Your Life – ://liveamoment.org
Conclusion
Autobà, the genus of moths introduced by Francis Walker in 1863, stands as a testament to the vast diversity and beauty found within the insect world. These unique creatures, with their intricate taxonomy and fascinating adaptations, continue to capture the attention of entomologists and nature enthusiasts alike.
As we delve deeper into understanding Autobà moths, we uncover not just a glimpse into the past work of eminent scientists like Walker but also an opportunity to explore new frontiers in research and conservation efforts. By shedding light on their distribution, habitat preferences, behaviors, and potential threats faced by these species, we pave the way for future studies that may help protect them from extinction.
With ongoing advancements in technology and increased awareness about biodiversity conservation, there is hope for preserving Autobà populations for generations to come. By continuing our exploration into this remarkable genus and supporting initiatives aimed at safeguarding their habitats, we can ensure that these enchanting moths remain a part of our natural heritage.
Let us embrace the wonder of Autobà moths as a reminder of the delicate balance that exists in nature and strive towards a future where they thrive alongside us on this planet Earth.